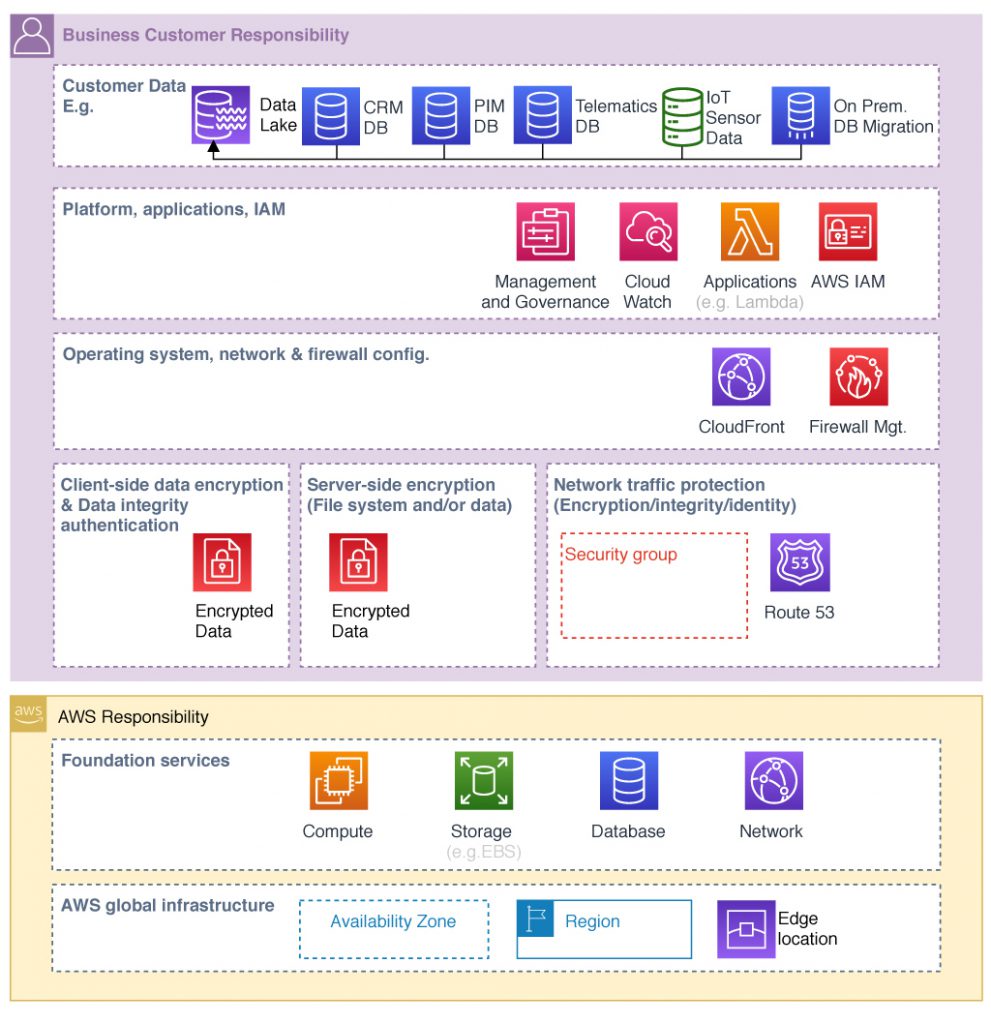
Security, a shared responsibility between Public Service Provider and the Business Customer.
Shared responsibilities
Security responsibility of the cloud infrastructure include:
o Design for security (physical structure and the software layer regulatory
compliance & security)
o Constantly monitored (monitoring of security incident or compromise)
o Highly automated (responses are highly automated)
o Highly available
o Highly accredited (consequences: physical environments are highly
accredited)
Security responsibility of AWS for the cloud means a framework build for:
o Hosts, networks, software, facilities
o Protection of AWS global infrastructure
o Availability of 3rd-party audit reports
But the business customer is also responsible for security in his layers. For example AWS provides a raw unformatted device for storage and the customer has to consider what data should be stored, which AWS services to use, in which region to store and mirror the data, in what content format and structure and who has access. How is the data delivered in transit and in rest. How to store, will it encrypted and how long it should be stored?
Least necessary privileges is the best practice only need to have access not nice to have. The rule configuration is one core customer responsibility. In a holistic view we end in a shared responsibility model.
Unmanaged Services
Different industries and businesses have a variety of specific security requirements, only the business owner could know. The customer own everything on top of a virtual server. The customer owns likewise everything you format on top of a data volume, like an AMAZON EBS. AWS provides a raw device (Unmanaged Services) configured for security by the customer. Using Unmanaged Services the customers takes the most responsibility for the services.
Managed Services
For the Managed Services AWS takes over some of the tasks, to provide security. E.g. in the operation systems database patching & installation, firewall configuration, disaster recovery is managed by AWS. AWS surfaces the customer database into his Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and it get’s the network isolation and protection of the customer.
AWS manage the virtual machine, on which SQLServer, MySQL, PostgreSQL or Oracle is running. In this case the responsibility is different shared: Operating systems and server are the job of AWS. The customer is managing access to the data base server. Likewise on AMAZON DynamoDB, S3, RDS, the customer don’t configure the servers on which those application environments run.
Unmanaged Services
o Amazon EC2
o Amazon EBS
Managed Services
o Amazon RDS
o AMAZON S3
o Amazon DynamoDB
Operations
o Guest OS patching
o Database patching
o Firewall configuration
o Disater recovery
o User data
And if you follow a multi cloud approach, you need to align the security guidline across all Public Cloud Provider (PCP), you integrate in your cloud infrastructure. But multi cloud solution is an other topic to discuss.